
Tesla’s Model Y and Model 3 exportation from Gigafactory Shanghai accounts for half of China’s electric vehicle exportation during the first half of 2022.
When Tesla first announced its plan to build a giant electric car factory in Shanghai, CEO Elon Musk said it was solely to supply China’s local demand for electric vehicles and wouldn’t export any vehicle to other markets.
But it didn’t end up turning out that way.
Tesla was extremely successful in ramping up production at Gigafactory Shanghai, which became the most productive electric vehicle factory in the world at an incredible pace.
In 2021, Tesla decided to take advantage of the production rate and turned Gigafactory Shanghai into its “export hub.”
Now the automaker had a tough first half of 2022 in China due to Gigafactory Shanghai being shut down for a significant part of Q2 due to lockdowns in the city.
Despite those difficulties, Tesla’s exports account for half of China’s electric vehicle exports during the first half of the year according to data compiled by CnEVPost:
Tesla’s Shanghai plant exported 97,182 vehicles in the first half of the year, accounting for 48 percent of all NEVs exported from China in the same period, according to data from the China Passenger Car Association (CPCA) monitored by CnEVPost.
China refers to all non-gas-powered vehicles as “new energy vehicles” (NEV), but electric cars account for most of those.
Here are Tesla’s historical exports from China:
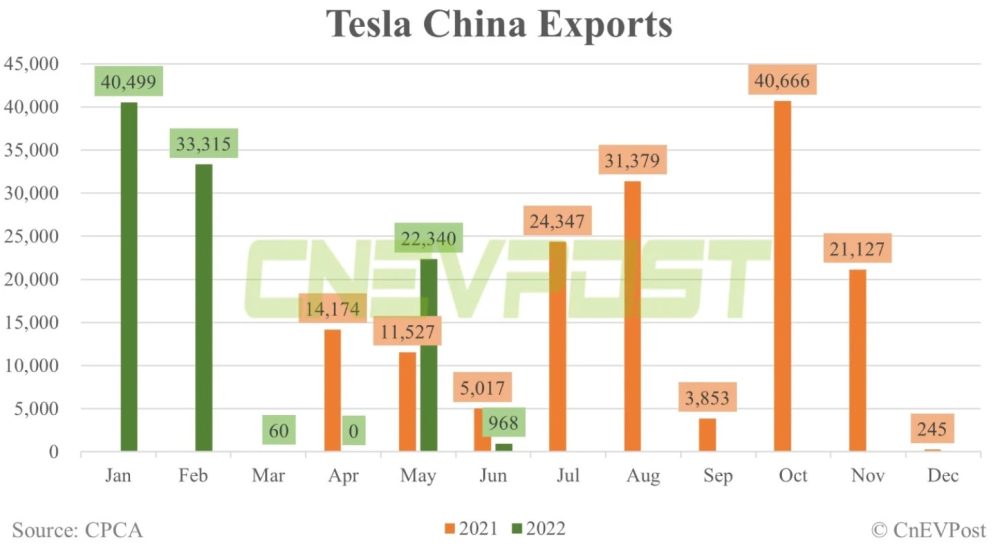
Historically, Western markets have been reticent to buy cars that were built in China even if they were built by major American or European automakers, but things are changing and especially for electric vehicles.
But now Tesla, Volvo, BMW, and Polestar are all exporting electric cars from China and having success with this model.
It’s a trend that started before 2020, but it has been ramping up fast over the last two years, and it is expected to continue.
FTC: We use income earning auto affiliate links. More.







Comments